Diamond Education
The more you know about diamonds, the more you’ll appreciate your diamond purchased from the Jewelry Exchange. To help you make an informed decision, we have listed below some important information that you should know before purchasing your next diamond.
The 4 C's of Diamonds
The 4Cs of diamonds are essential characteristics used to evaluate their quality and value. Carat weight measures the size of the diamond, while cut determines how well it reflects light, impacting its brilliance and sparkle. Color refers to the diamond’s hue, ranging from colorless to varying degrees of yellow or brown. Clarity assesses the presence of internal and external flaws, affecting the diamond’s transparency. By considering the interplay of carat weight, cut, color, and clarity, buyers can make informed decisions when choosing a diamond, finding the perfect balance to suit their preferences and budget.
Here at the Jewelry exchange we can help customers make informed choices that align with their preferences and financial considerations when selecting a diamond from contacting our sales or email. Or come on in and Find a Jewelry Store Near You! We have 12 stores nationwide across the United States dedicated in helping customers finding the right diamond for them.
Cut
The cut of a diamond refers to how well it has been shaped and faceted. It is one of the most critical factors influencing a diamond’s appearance and beauty. The quality of the cut directly impacts how effectively the diamond reflects and refracts light, resulting in its sparkle and brilliance. A well-cut diamond allows light to enter through the table (the flat top surface) and then reflects it from facet to facet, directing the light back out through the crown (the upper part). When light is maximized and properly dispersed, the diamond exhibits a captivating play of light, often described as fire, brilliance, and scintillation.
Color
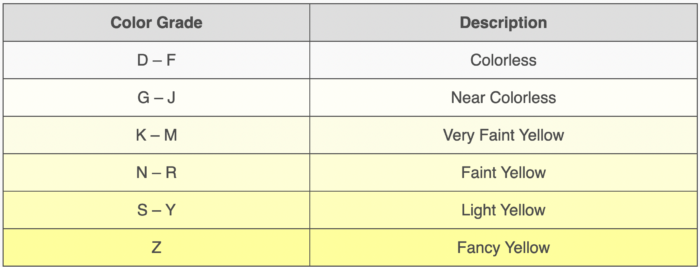
Diamonds come in various colors, ranging from colorless to light yellow or brown. The GIA color scale grades diamonds from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown). The best and most valuable diamonds are typically colorless or near-colorless, falling in the D to J range.
Clarity
Clarity refers to the presence of internal and external flaws, or inclusions, within a diamond. Inclusions are natural imperfections that occurred during the diamond’s formation deep within the earth or during its journey to the surface. Diamonds with higher clarity grades (FL, IF, VVS) are rarer and more valuable because they have fewer inclusions, resulting in better light performance and overall appearance. However, diamonds with lower clarity grades (SI and below) can still be beautiful and appealing, especially when their inclusions are not easily visible to the naked eye.
Carat Weight
Carat weight is the measurement of a diamond’s size and is expressed in carats. One carat is equivalent to 200 milligrams or 0.2 grams. Larger diamonds are generally rarer and more valuable, but the value of a diamond is not solely determined by its carat weight. The other 3Cs (cut, color, and clarity) also play a significant role in a diamond’s overall quality and price.
It’s essential to note that carat weight is not the same as the physical dimensions of the diamond. Different diamonds can have the same carat weight but appear slightly different in size due to variations in cut and shape.
Diamond Shapes
Diamonds come in various shapes, each with its unique characteristics and appeal. The shape of a diamond refers to its outline when viewed from the top, and it is distinct from the cut, which refers to how well the diamond’s facets are proportioned and arranged.
Certification
The Jewelry Exchange sends diamonds to three different gemological research laboratories for grading: GIA, EGL USA, and AGS. Each lab has its own grading standards, so when comparing diamonds, we recommended that you compare diamonds with like certificates.
GIA certifications are issued for diamonds and colored gemstones that have undergone evaluation and grading by GIA’s gemologists at one of their accredited laboratories. These certifications provide detailed information about the gemstone’s 4Cs (carat weight, cut, color, and clarity) and other important characteristics, giving consumers confidence in the quality and authenticity of the stone.
Have Any Questions?
Contact us by our phone number at (800) 431-9393 or email at [email protected]
We also have live chat during available business hours.
Find Your Jewelry Store Today!
The Jewelry Exchange have 12 Jewelry Stores throughout the United States.
Diamond Cut
What Part Is The Cut Of A Diamond?
The cut of a diamond refers to how well it has been shaped and faceted. It is one of the most critical factors influencing a diamond’s appearance and beauty. The quality of the cut directly impacts how effectively the diamond reflects and refracts light, resulting in its sparkle and brilliance. A well-cut diamond allows light to enter through the table (the flat top surface) and then reflects it from facet to facet. Directing the light back out through the crown (the upper part). When light is maximized and properly dispersed, the diamond exhibits a captivating play of light, often described as fire, brilliance, and scintillation.
Here at the Jewelry exchange we can help customers make informed choices that align with their preferences and financial considerations when selecting a diamond cut from contacting our sales or email. Or come on in and Find a Jewelry Store Near You! We have 12 stores nationwide across the United States dedicated in helping customers finding the right diamond for them.
What Cut of Diamond Should I Get?
Guidance on choosing the right diamond cut can be quite confusing. Finding the right cut is based on your budget. All diamond shapes have their unique beauty, some may be more affordable than others. Explore our various cut options, including round, princess, cushion, and emerald cuts, to find the one that suits your style and budget. A well-cut diamond can still exhibit exceptional brilliance and sparkle, even if it falls within a more budget-friendly range.
The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) grades diamond cuts on the following scale:
- Excellent
- Very Good
- Good
- Fair
- Poor
An “Excellent” or “Ideal” cut is preferred for its exceptional light performance, while a “Poor” cut can result in a dull and lifeless appearance.
Aspects of a Well-Cut Diamond:
- Brilliance: The intense white light reflected from a diamond’s surface, creating its sparkle.
- Fire (Dispersion): The colorful flashes of light that occur as white light is broken into spectral hues.
- Scintillation: The pattern of contrasting light and dark areas seen when a diamond or the light source moves, adding liveliness to its appearance.
Excellent Cut: The highest grade for a diamond’s cut, reflecting exceptional light performance and maximum brilliance.
Very Good Cut: A high-quality cut with excellent light reflection and impressive sparkle, offering great value.
Good Cut: A well-proportioned cut that reflects a considerable amount of light, providing good sparkle and brilliance.
Fair Cut: A cut that allows some light to escape, resulting in reduced sparkle and brilliance compared to higher grades.
Poor Cut: A cut that significantly lacks proper proportions, leading to minimal light reflection and diminished beauty.
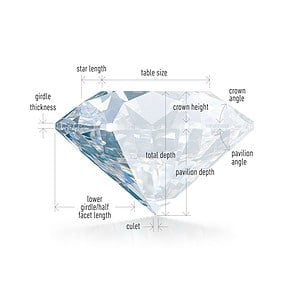
The Key Parts of A Diamond
The anatomy of a diamond consists of several key components. The crown is the top part, with facets that help reflect and refract light. Below the crown is the girdle, the widest part that separates the crown from the pavilion, the lower section. The pavilion includes facets that reflect light back through the crown, contributing to the diamond’s brilliance. The culet is the small facet at the bottom tip of the pavilion. Lastly, the table is the large, flat facet on the top of the diamond. A diamond’s proportions and symmetry significantly impact its beauty and value, with well-cut diamonds optimizing light performance and enhancing their overall appearance.
Is the cut and shape the same thing?
Cut and shape are two distinct characteristics of a diamond. The shape refers to the diamond’s outline when viewed from the top, such as round, princess, emerald, etc. Cut, on the other hand, refers to how well the diamond’s facets are proportioned and arranged, impacting its brilliance and sparkle. While shape is a matter of personal preference, cut directly affects a diamond’s beauty and light performance.
Have Any Questions?
Contact us by our phone number at (800) 431-9393 or email at [email protected]
We also have live chat during available business hours.
Find Your Jewelry Store Today!
There at the Jewelry exchange we can help customers make informed choices that align with their preferences and financial considerations when selecting a diamond cut from contacting our sales or email. Or come on in and Find a Jewelry Store Near You! We have 12 stores nationwide across the United States dedicated in helping customers finding the right diamond for them.
Color
Diamonds come in various colors, ranging from colorless to light yellow or brown. The GIA color scale grades diamonds from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown). The best and most valuable diamonds are typically colorless or near-colorless, falling in the D to J range.
Colorless diamonds allow more light to pass through and are more desirable because they exhibit a pure and brilliant white appearance. As you move down the color scale, the yellow or brown tint becomes more noticeable, impacting the diamond’s sparkle and value.
It’s worth noting that beyond the Z range, diamonds with intense and vivid colors are classified as “Fancy Colored Diamonds” and have a different grading system.
Here at the Jewelry exchange we can help customers make informed choices that align with their preferences and financial considerations when selecting a diamond that’s the right color for them. By contacting our sales or email, or our Jewelry Stores. Come on in and Find a Jewelry Store Near You! We have 12 stores nationwide across the United States dedicated in helping customers finding the right diamond for them.
Diamond Color Affects The Beauty Of A Diamond
Diamond color directly impacts a diamond’s visual appeal and value. The color grade, ranging from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown), determines the presence of any tint in the stone. A diamond with a higher color grade (e.g., D or E) will appear bright, brilliant, and colorless, allowing more light to pass through and reflecting it back as white light. In contrast, a lower color grade (e.g., J or K) will show a visible yellowish or brownish tint, diminishing its sparkle and overall beauty. For example, a D color diamond will display a dazzling, pure white appearance, while a J color diamond will exhibit a warmer, slightly yellow hue. The less color a diamond has, the more desirable and valuable it generally becomes.
Different Shapes Of Diamonds Can Change The Diamond Color
The shape of a diamond itself does not influence its color grade. The color grade is determined by the presence of any tint within the diamond, regardless of its shape. However, the perceived color of a diamond can be affected by its shape due to how light interacts with the stone’s facets. Round brilliant cut diamonds, with their numerous facets, may show color more prominently, while fancy-shaped diamonds like princess or cushion cuts might mask color better, dispersing any tint more effectively. Nevertheless, the actual color grade remains consistent for the diamond, regardless of its shape.
Setting Also Impacts Color Appearance In A Diamond
The setting of a diamond can influence how its color is perceived by affecting the amount of light that enters the stone. A white metal setting, such as platinum or white gold, can enhance the appearance of a colorless or near-colorless diamond, making it appear even whiter and more brilliant. On the other hand, a yellow or rose gold setting can complement a lower color grade diamond by masking any slight yellowish or brownish tint, making it appear warmer and more harmonious with the metal. The setting’s color contrast with the diamond can create visual illusions, subtly impacting how the diamond’s color is perceived by the observer.
The GIA White Diamonds Color-Grade Scale Is What We Use For Our Diamonds
The GIA White Diamonds Color-Grade Scale is a widely used grading system for evaluating the color of white diamonds. It ranges from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown). The scale categorizes diamonds based on the presence of any color or tint in the stone. Diamonds in the D to F range are considered colorless, displaying no perceptible color, while diamonds in the G to J range are classified as near-colorless, with minimal traces of color visible only to trained gemologists. As you move down the scale from K to Z, the color becomes more noticeable, impacting the diamond’s overall appearance and value. The GIA color-grading system ensures consistency and helps consumers and the diamond industry make informed decisions about diamond quality and value.
Which Diamond Color Is Best?
Helpful Hint: When Diamond prices increase in alphabetical order. For example, a diamond with a D color grade is more expensive than a diamond with a F color grade.
The “best” diamond color is a subjective choice and depends on personal preferences and the overall appearance desired. Generally, diamonds with higher color grades (colorless or near-colorless) in the D to G range are considered more desirable and valuable. However, the choice of the “best” diamond color ultimately depends on individual taste, budget, and the setting in which the diamond will be placed. Some people prefer the icy brilliance of colorless diamonds (D, E, or F), while others may appreciate the warmth of near-colorless diamonds (G, H, or I). The key is to find a diamond that appeals to you and complements your style and preferences.
Have Any Questions?
Contact us by our phone number at (800) 431-9393 or email at [email protected]
We also have live chat during available business hours.
Find Your Jewelry Store Today!
The Jewelry Exchange have 12 Jewelry Stores throughout the United States.
Clarity
Diamond clarity is all about checking for any imperfections or tiny things inside or on the surface of a diamond. These imperfections are called inclusions and blemishes. They’re like little birthmarks or marks that happened when the diamond was forming deep underground. Jewelers use special tools to see these flaws up close. The clarity grade tells us how many and how big these imperfections are. The better the clarity grade, the fewer flaws there are, and the more brilliant and valuable the diamond is. But don’t worry, some diamonds with a lower clarity grade can still look amazing to the naked eye, so it’s all about finding one that looks perfect to you!
If you need help finding the right diamond for you, The Jewelry exchange can help! We have 12 Jewelry Stores nationwide across the U.S and we are dedicated to help customers be satisfied in finding their beautiful diamond. Find a Jewelry store near you today or contact us!
We Use The GIA Clarity Scale Which Is The Industry Standard
Understanding the 4Cs is essential when purchasing a diamond, as it helps you make an informed decision based on your preferences, budget, and desired appearance of the diamond. A balanced combination of these four factors will result in a stunning and valuable diamond that suits your needs and tastes.
Clarity refers to the presence of internal and external flaws, or inclusions, within a diamond. Inclusions are natural imperfections that occurred during the diamond’s formation deep within the earth or during its journey to the surface.
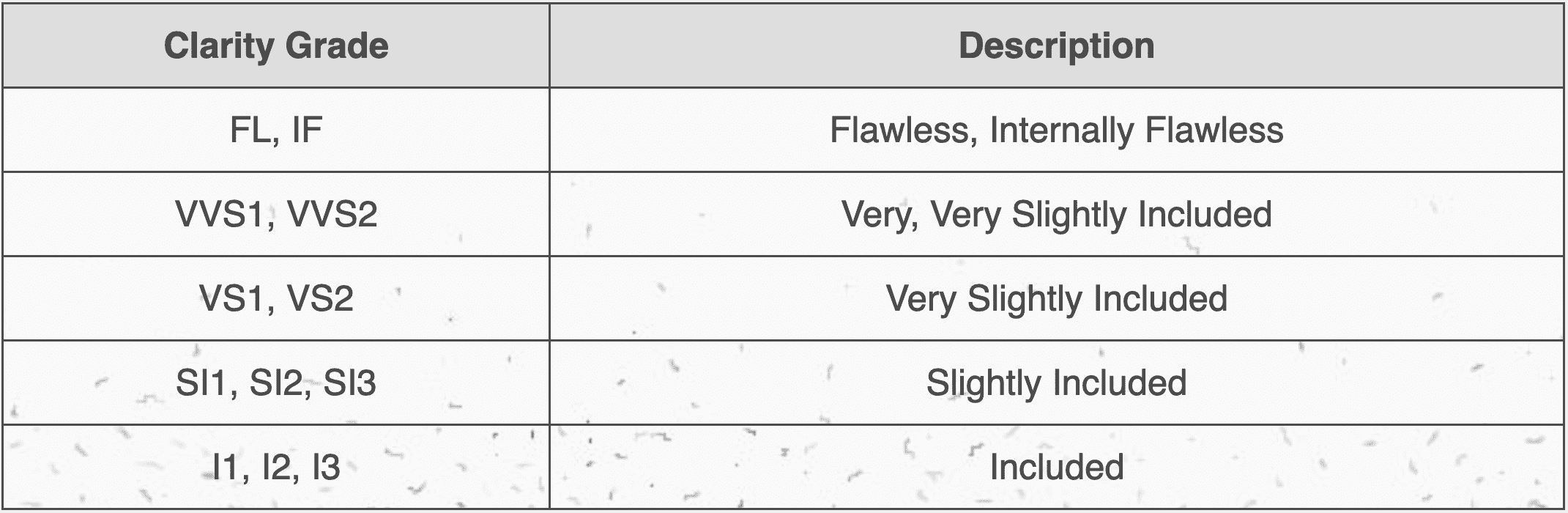
The GIA clarity scale grades diamonds as follows:
- Flawless (FL): No inclusions or blemishes visible under 10x magnification.
- Internally Flawless (IF): No inclusions visible under 10x magnification, but minor surface blemishes may be present.
- Very, Very Slightly Included (VVS1 and VVS2): Inclusions are difficult to see under 10x magnification.
- Very Slightly Included (VS1 and VS2): Inclusions are visible under 10x magnification but may be challenging to detect.
- Slightly Included (SI1 and SI2): Inclusions are noticeable under 10x magnification.
- Included (I1, I2, and I3): Inclusions are visible to the naked eye and can affect the diamond’s brilliance and transparency.
Diamonds with higher clarity grades (FL, IF, VVS) are rarer and more valuable because they have fewer inclusions, resulting in better light performance and overall appearance. However, diamonds with lower clarity grades (SI and below) can still be beautiful and appealing, especially when their inclusions are not easily visible to the naked eye.
Aspects of Clarity
Clarity: Clarity refers to the presence of inclusions (internal flaws) and blemishes (external flaws) within or on the surface of a diamond. The clarity grade assesses the number, size, location, and visibility of these imperfections.
Inclusions: Inclusions are internal flaws in a diamond, such as tiny crystals, feathers, or other minerals that were trapped during the diamond’s formation.
Blemishes: Blemishes are external flaws on the diamond’s surface, like scratches, nicks, or naturals (remnants of the diamond’s original crystal shape).
Eye-Clean: Diamonds with lower clarity grades (like SI or I) may be “eye-clean,” meaning their flaws are not visible to the naked eye without magnification.
What Are Some Popular Clarity Gradings for Diamonds?
Popular clarity gradings for diamonds include SI1 and SI2 (Slightly Included), which have slight inclusions that may be visible under magnification but are usually not noticeable to the naked eye. These grades offer a good balance between quality and price. VS1 and VS2 (Very Slightly Included) diamonds have very minute inclusions that are difficult to see under magnification, providing excellent value with high-quality diamonds. IF (Internally Flawless) diamonds have no internal inclusions visible under magnification, making them extremely rare and highly valued for their pristine clarity. VVS1 and VVS2 (Very, Very Slightly Included) diamonds have nearly invisible inclusions under magnification, offering exceptional quality and transparency. Each of these clarity grades provides various options for buyers based on their preferences and budget, ensuring there’s a beautiful diamond for every taste and style.
Why SI Diamonds And VS Diamonds are Best Valued?
SI (Slightly Included) and VS (Very Slightly Included) diamonds are considered the best value because they offer an appealing balance between quality and price. These clarity grades have minor inclusions that are not easily visible to the naked eye but may be seen under 10x magnification. Despite the slight inclusions, these diamonds often appear eye-clean, looking beautiful and brilliant in jewelry settings. SI and VS diamonds are more affordable than higher clarity grades, allowing buyers to allocate their budget towards other essential factors like cut, color, and carat weight. Their widespread availability makes it easier to find a wide selection of diamonds with these clarity grades, offering various options for buyers seeking stunning diamonds at a more attractive price point.
Have Any Questions?
Contact us by our phone number at (800) 431-9393 or email at [email protected]
We also have live chat during available business hours.
Find Your Jewelry Store Today!
The Jewelry Exchange have 12 Jewelry Stores throughout the United States.
Carat Weight
Carat weight is the measurement of a diamond’s size and is expressed in carats. One carat is equivalent to 200 milligrams or 0.2 grams. Larger diamonds are generally rarer and more valuable, but the value of a diamond is not solely determined by its carat weight. The other 3Cs (cut, color, and clarity) also play a significant role in a diamond’s overall quality and price.
It’s essential to note that carat weight is not the same as the physical dimensions of the diamond. Different diamonds can have the same carat weight but appear slightly different in size due to variations in cut and shape.
Here at the Jewelry exchange we can help customers make informed choices that align with their preferences and financial considerations when selecting a diamond that’s the right carat weight for you. By contacting our sales or email, or our Jewelry Stores. Come on in and Find a Jewelry Store Near You! We have 12 stores nationwide across the United States dedicated in helping customers finding the right diamond for them.
Carat Weight Measures The Size Of A Diamond. Usually The Size Of A Diamond Impacts Cost
Carat weight directly impacts the size of a diamond. The higher the carat weight, the larger the diamond will be physically. Carat weight is a standardized measurement that quantifies a diamond’s weight and, consequently, its size. As carat weight increases, more material is added to the diamond, making it physically larger and more substantial.
For example, a one-carat diamond will be bigger than a half-carat diamond, and a two-carat diamond will be even larger than a one-carat diamond. However, it’s important to note that carat weight alone does not determine a diamond’s overall appearance or beauty. The visual impact of a diamond is influenced by other factors like cut, color, and clarity, which also play crucial roles in determining a diamond’s brilliance and sparkle. Therefore, when considering a diamond, it’s essential to strike a balance between carat weight and the other factors to find a diamond that meets your desired size and appearance while still looking stunning and brilliant.

How Does Carat Impact Diamond Sizes?
As the carat weight increases, so does the size of the diamond. Larger diamonds are generally rarer and more valuable because they are less commonly found in nature. Carat weight is one of the four Cs (carat, cut, color, and clarity) used to evaluate a diamond’s quality and value. It’s important to note that carat weight alone does not determine a diamond’s overall beauty and desirability. The cut, color, and clarity also play significant roles in the diamond’s appearance and worth. When choosing a diamond, it’s essential to consider the right balance of the four Cs based on your preferences, budget, and the overall look you desire.
The 4 Things To Know About Carat Weight
- Carat Weight: Carat weight measures the size and weight of a diamond, with one carat equal to 200 milligrams or 0.2 grams. Larger diamonds generally have higher carat weights, making them more valuable and rarer.
- Size and Appearance: Carat weight directly affects the physical size of a diamond. As the carat weight increases, the diamond will look larger. However, carat weight alone does not determine a diamond’s overall appearance or beauty; factors like cut, color, and clarity also significantly influence its visual appeal.
- Price and Value: Carat weight plays a crucial role in a diamond’s price and value. Larger diamonds with higher carat weights are typically more expensive per carat compared to smaller ones. However, factors like cut, color, and clarity also affect a diamond’s price, and two diamonds with the same carat weight can vary significantly in value based on these other characteristics.
- Personal Preference and Budget: When choosing a diamond, it’s essential to consider your personal preference for size and appearance. Keep in mind that a larger carat weight might be impressive, but it might not fit your budget or style. Finding the right balance between carat weight, cut, color, and clarity allows you to select a diamond that suits your taste and budget while maximizing its beauty and value.
The Difference Between Karat vs. Carat
Carat and karat are two different terms used in different contexts. Carat is a unit of weight used to measure the size of gemstones, including diamonds. One carat is equivalent to 200 milligrams. It helps determine how big a diamond or gemstone appears. On the other hand, karat is a unit used to measure the purity of gold in jewelry. Pure gold is 24 karats, but most gold jewelry is made with alloys, so 18-karat gold, for example, means it is 75% pure gold and 25% other metals. In summary, carat measures the size of gemstones, and karat measures the purity of gold in jewelry.
Have Any Questions?
Contact us by our phone number at (800) 431-9393 or email at [email protected]
We also have live chat during available business hours.
Find Your Jewelry Store Today!
The Jewelry Exchange have 12 Jewelry Stores throughout the United States.
Diamond Shape
Diamonds come in various shapes, each with its unique characteristics and appeal. The shape of a diamond refers to its outline when viewed from the top, and it is distinct from the cut, which refers to how well the diamond’s facets are proportioned and arranged.
Here at the Jewelry exchange we can help customers make informed choices that align with their preferences and financial considerations when selecting a diamond that’s the right shape for you By contacting our sales or email, or our Jewelry Stores. Come on in and Find a Jewelry Store Near You! We have 12 stores nationwide across the United States dedicated in helping customers finding the right diamond for them.
What’s The Relationship Between Shape And Color?
The color of a diamond is independent of its shape, meaning a diamond’s color grade remains the same, regardless of its shape. For example, a round diamond and a princess-cut diamond with the same color grade will have the same color appearance.
However, the way light interacts with a diamond can slightly affect the perception of color based on its shape. For instance, round diamonds with numerous facets may show color more prominently, while fancy-shaped diamonds with fewer facets might disperse color differently, making any tint less noticeable.
Diamond Clarity And Shape Impacts
Regardless of the diamond shape, its clarity grade is determined by the number, size, location, and visibility of inclusions and blemishes. The same clarity grading standards are applied to all diamond shapes, ensuring consistency in evaluating a diamond’s clarity.
While the diamond’s shape does not affect its clarity grade, certain diamond shapes, like round brilliants with numerous facets, might show inclusions more prominently than fancy-shaped diamonds with fewer facets. However, this impact on visibility is relatively minor, and the clarity grade remains consistent across all shapes.
When choosing a diamond, it’s essential to consider both its shape and clarity grade. The decision ultimately depends on personal preferences, budget, and the overall appearance desired for the jewelry piece. Opting for a well-balanced combination of shape and clarity ensures you get a stunning diamond that suits your style and preferences.
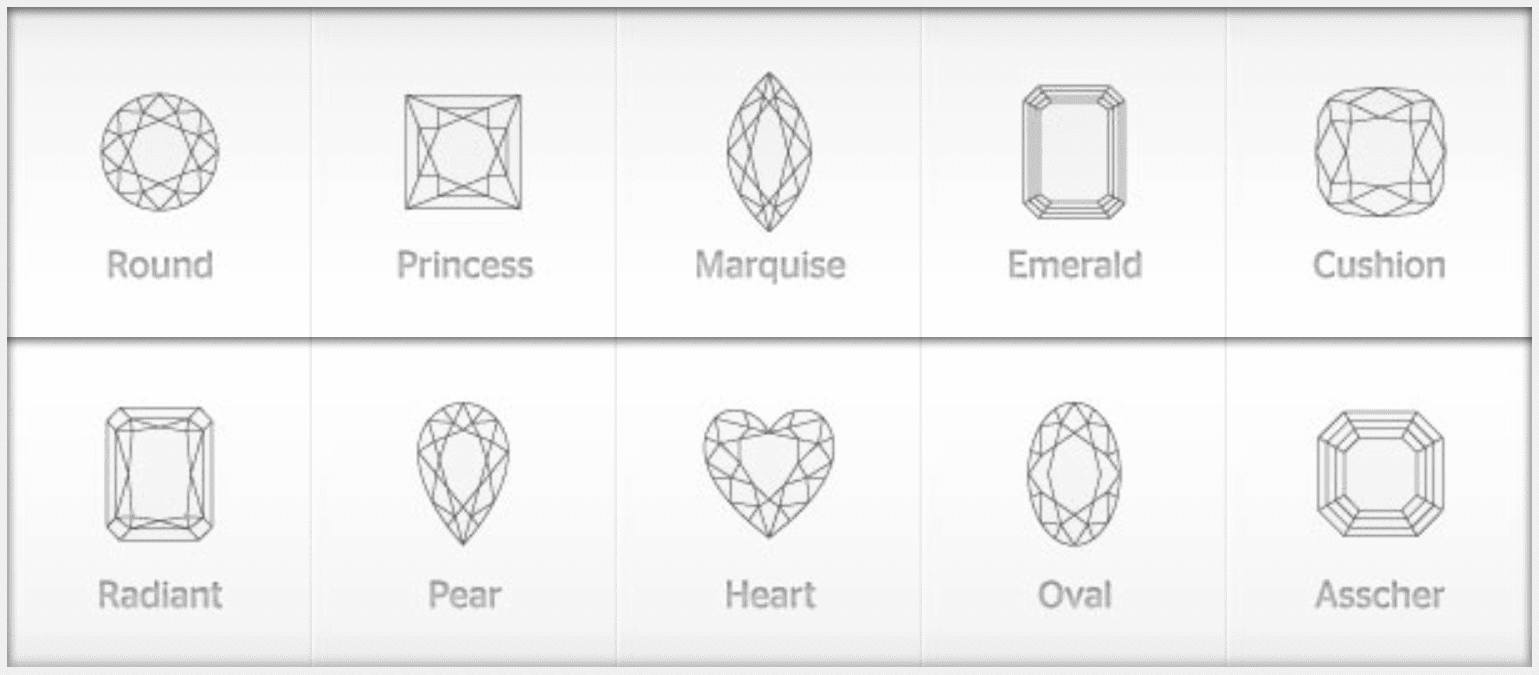
Some Popular Shapes Of Diamonds
There are also other unique and fancy shapes, such as heart, trilliant (triangle), baguette, and radiant cuts with rounded corners. When choosing a diamond shape, consider your personal preferences, style, and the setting in which the diamond will be placed. Each shape has its own beauty and charm, making it essential to find the one that best suits your taste and design preferences.
Round Brilliant, The classic and most popular diamond shape, known for its exceptional brilliance and sparkle. Princess Cut, A square-shaped diamond with sharp corners, offering a contemporary and brilliant appearance. Emerald Cut, A rectangular shape with step-cut facets, known for its elegant and sophisticated look. Asscher Cut, Similar to the emerald cut but with a square shape and an Art Deco appeal. Cushion Cut, A square or rectangular shape with rounded corners, combining brilliance with a romantic feel. Radiant Cut, A square or rectangular shape with brilliant facets, providing exceptional sparkle. Pear Shape, A teardrop-shaped diamond with a unique and elegant appearance. Marquise Cut, An elongated diamond with pointed ends, creating the illusion of longer fingers. Oval Shape, A modified round brilliant cut, appearing elongated and elegant. Heart Shape, A romantic choice with a distinctive heart outline.
Have Any Questions?
Contact us by our phone number at (800) 431-9393 or email at [email protected]
We also have live chat during available business hours.
Find Your Jewelry Store Today!
The Jewelry Exchange have 12 Jewelry Stores throughout the United States.

Certification
The Jewelry Exchange sends diamonds to three different gemological research laboratories for grading: GIA, EGL USA, and AGS. Each lab has its own grading standards, so when comparing diamonds, we recommended that you compare diamonds with like certificates.
GIA certifications are issued for diamonds and colored gemstones that have undergone evaluation and grading by GIA’s gemologists at one of their accredited laboratories. These certifications provide detailed information about the gemstone’s 4Cs (carat weight, cut, color, and clarity) and other important characteristics, giving consumers confidence in the quality and authenticity of the stone.
Here at the Jewelry exchange we can help customers make informed choices that align with their preferences and financial considerations when selecting a diamond that has the right certification for you. By contacting our sales or email, or our Jewelry Stores. Come on in and Find a Jewelry Store Near You! We have 12 stores nationwide across the United States dedicated in helping customers finding the right diamond for them.
What Is Diamond Certification?
Diamond certification, also known as a diamond grading report or diamond dossier, is an official document issued by a reputable gemological laboratory that provides a detailed and unbiased assessment of a diamond’s quality and characteristics. The certification is typically performed by highly trained gemologists who evaluate the diamond based on the 4Cs: carat weight, cut, color, and clarity, as well as other factors like polish, symmetry, fluorescence, and measurements.
The certificate includes crucial information about the diamond’s measurements, proportions, grade, and any imperfections (inclusions and blemishes) found under magnification. It serves as a reliable and independent verification of a diamond’s authenticity, quality, and value. Certifications from well-known laboratories, such as the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) or the American Gem Society (AGS), are highly regarded in the industry, providing buyers with confidence in their diamond purchase.

Understanding The Parts Diamond Grading
Understanding diamond certification involves familiarizing yourself with the information provided in the certification report and knowing what each section means. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you understand a diamond certification:
- Review the Laboratory: Check which gemological laboratory issued the certification. Reputable labs like GIA, AGS, EGL, or IGI are widely recognized and respected in the industry.
- Verify the Diamond Details: Look for information about the diamond’s 4Cs (carat weight, cut, color, and clarity). Understand the specific grades assigned to each category, such as Excellent for cut, D for colorless, VVS1 for clarity, etc.
- Examine the Diamond Plot: The certification often includes a diagram or plot showing the diamond’s internal and external characteristics (inclusions and blemishes). Familiarize yourself with these markings and their locations.
- Check for Additional Features: Some certifications may include details on fluorescence, polish, symmetry, measurements, and other relevant information.
- Understand the Terminology: Learn about the technical terms used in the certification. Online resources and glossaries can help clarify any unfamiliar language.
Why Is It Important To Get A Diamond Grading?
Getting a diamond grading is crucial for several reasons. A diamond grading report, provided by reputable gemological laboratories like GIA or AGS, offers an unbiased and comprehensive assessment of a diamond’s quality, including its carat weight, cut, color, and clarity. This certification ensures that you are receiving the exact diamond you paid for, preventing misrepresentations or scams. It serves as a unique fingerprint for the diamond, verifying its authenticity and distinguishing it from others. With this detailed information, you can make an informed decision about the diamond’s value and suitability for your preferences and budget. Additionally, having a diamond grading report is beneficial for resale and insurance purposes, as it provides potential buyers or jewelers with confidence in the diamond’s quality and allows for fair pricing. Ultimately, the report promotes trust and transparency in the diamond industry, ensuring that you are making a secure and informed investment in a valuable and genuine diamond.
Have Any Questions?
Contact us by our phone number at (800) 431-9393 or email at [email protected]
We also have live chat during available business hours.
Find Your Jewelry Store Today!
The Jewelry Exchange have 12 Jewelry Stores throughout the United States.